2 mva transformer manufacturers
An Authorized 2 mva dry type transformer, 2 mva cast resin transformer suppliers in africa, view 2000 kva transformer price in india
A 2000 kva transformer amps is a electrical device which can transfer electrical energy from one electrical circuit to one or more than one circuits. This 2 mva cast resin transformer is an electrical device that is known to be passive. A varying current in any one coil of the 2000 kva transformer could produce a varying magnetic flux.
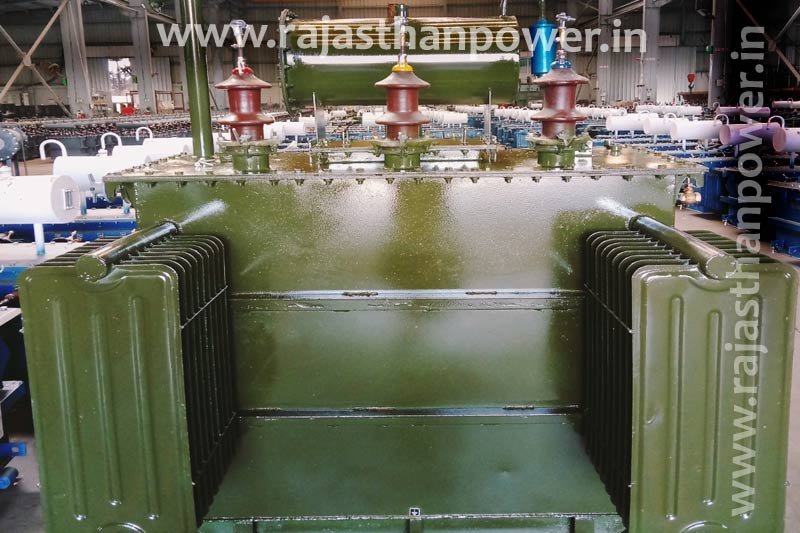


2 mva transformer manufacturers

2000 kva transformer

2 mva dry type transformer
Looking For 2 mva pad mounted transformer, 2000 kva dry type transformer Exporter in india, view 2000 kva transformer price.
This magnetic flux, in the 2 mva transformer can in turn, induce a varying electromotive force across any other coils which are wound around the same core. Click here to check the rate of cost of 2 mva transformer. At Rajasthan Powergen Transformer P. Ltd., we offer one of the most competitive 2 mva transformer price in India. Click here to find out the 2000 kva transformer price. We are one of the leading 2 mva transformer manufacturers in India.
Electrical energy can be transferred between possibly many coils of the 2 mva transformer specification, without a metallic connection between these two circuits. Since all energized connection points in a pad mounted 2 mva transformer full load current have been securely enclosed in a grounded metal housing, a 2000 kva pad mount transformer can be installed in places which do not have room for a fenced enclosure.
Typically, the 2 mva pad mounted transformer is used with underground electric power distribution lines at service drops. Here the pad mount 2000 kva transformer is used to step down the primary voltage on the line to the secondary lower voltage which is then supplied to utility customers.
A single 2 mva transformer oil quantity could be used to serve one large building, or many homes. Click here to find out the 2 mva transformer weight as well as the 2 mva transformer dimensions and the 2 mva transformer current rating. A 2000 kva dry type transformer is a type of transformer which generally never uses any insulating liquid in cases where the winding or core of the 2 mva dry type transformer have been immersed in liquid. Rather, the windings as well as the core of the 2 mva dry type transformer dimensions are to be kept within a sealed tank that is pressurized with air.
Volt amperes are a unit utilized to describe the electrical load in engineering. Volt amperes can be abbreviated VA. You can also utilize metric prefixes such as "kilo-" and "mega-." It takes 1,000 volt amperes to rise to one kilo-volt ampere and 1,000,000 volt-amperes to equal one mega-volt ampere. Therefore, it takes 1,000 kilo-volt amperes to get one mega-volt ampere. Divide the number of kVA by 1,000 to convert to MVA. For example, in case you’ve got 438 kVA, isolate 438 by 1,000 to get 0.438 MVA
We are one of the leading transformer manufacturer company catering to different segments that require continuous power supply.We realize the challenges faced by companies that depend on continuous supply of power for their operations. In case of transformer breakdown, we offer our transformers for beneficiary for brief power generation with step-up capabilities. Through our group of talented and proficient professionals, we guarantee fast arrangement and productive execution with no respectful alterations required.
2 MVA = 2000kVA
The copper losses within the transformer are variable losses and are depends upon the current rating of the transformer and the iron losses are depending upon the voltage. Hence, the full losses in a transformer depends on the voltage and current appraisals of the transformer. In other words the full losses depends on the volt-ampere (VA) item only and not on the phase angle between voltage and current i.e. it is autonomous of load power factor. That’s why rating of transformer is continuously communicated in kVA or MVA.
| Basic Transformer Concept | oil-immersed, hermetic |
| Tank Design | Corrugated tank design, flexible cooling fins |
| Number of Phases | 3-phase |
| Rated Power | 2000 kVA |
| Method of Cooling | ONAN |
| Voltage Ratio | 10 000 / 400 V |
| Voltage Regulation | off-circuit tap changer |
| Tapping Range | +-2×2,5% |
| Various Voltage Ratio: | 10500/400 V 10250/400 V 10000/400 V 9750/400 V 9500/400 V |
| Frequency | 50 Hz |
| Temperature Rise | 60/65 K |
| Connection | Dyn5 |
| Impedance | 6,06% |
| Total Weight | 4340 kg |
| 2 mva transformer manufacturers export to | Uganda, Bangladesh, Nigeria, India, Nepal, Rwanda, Malaysia Tanzania, Kenya, Malawi, Africa |
| Other Ratings | 10, 16, 25, 50, 63, 100, 160, 200, 315, 500, 630, 750 kVA |
| all above transformer are | 11kV , 22kV, 33kV line |
| Efficiency | 3, 4, 5 Star or Level II, Level III |
For Final 2 mva transformer price in india Please Mail Us on info@rajasthanpower.in
Find Great Deals On 2 mva 11kv transformer, 2000 kva pad mount transformer, Check 2 mva transformer price
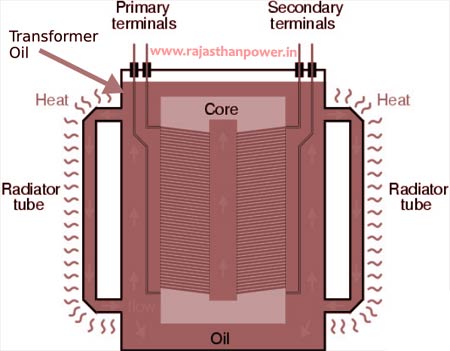
Transformer oil (moreover known as insulating oil) may be a uncommon type of oil which has fabulous electrical protection properties and is steady at high temperatures. Transformer oil is utilized in oil-filled electrical power transformers to insulate, stop arcing and corona release, and to disseminate the heat of the transformer (i.e. act as a coolant).
| Main Dimensions of the 300-2500 kVA Standard Transformers with Oil Expansion Tanks | |||||||||||||||
| Power | Max Voltage | Weight of Oil | Active Section Weight | Total Weight | Leng. A | Wid. B | Heig. C | D | F | ØG | L | M | N | S | T |
| kVA | kV | kg | kg | kg | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm |
| 2000 KVA | 6,3-11 | 1025 | 2730 | 4785 | 2265 | 1250 | 2255 | 1525 | 1000 | 200 | 70 | 310 | 400 | 372 | 200 |
| 15 | 1080 | 2765 | 4895 | 2270 | 1260 | 2160 | 1430 | 385 | |||||||
| 33 | 1185 | 2745 | 4985 | 2270 | 1275 | 2465 | 1635 | 485 | |||||||
Formulas Used In Calculation:
1-Phase KVA = Volts x Amps / 1000
1-Phase Amps = KVA / Volts x 1000
3-Phase KVA = Volts x Amps x 1.732 / 1000
3-Phase Amps = KVA / Volts / 1.732 x 1000
| Generator KVA Rating to Amperage Conversion Chart 80% POWER FACTOR |
|||||||||||
| kV•A | kW | 208V | 220V | 240V | 380V | 440V | 480V | 600V | 2400V | 3300V | 4160V |
| 6.3 KVA | 5 | 17.5 | 16.5 | 15.2 | 9.6 | 8.3 | 7.6 | 6.1 | |||
| 9.4 KVA | 7.5 | 26.1 | 24.7 | 22.6 | 14.3 | 12.3 | 11.3 | 9.1 | |||
| 12.5 KVA | 10 | 34.7 | 33 | 30.1 | 19.2 | 16.6 | 15.1 | 12 | |||
| 18.7 KVA | 15 | 52 | 49.5 | 45 | 28.8 | 24.9 | 22.5 | 18 | |||
| 25 KVA | 20 | 69.5 | 66 | 60.2 | 38.4 | 33.2 | 30.1 | 24 | 6 | 4.4 | 3.5 |
| 31.3 KVA | 25 | 87 | 82.5 | 75.5 | 48 | 41.5 | 37.8 | 30 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 4.4 |
| 37.5 KVA | 30 | 104 | 99 | 90.3 | 57.6 | 49.8 | 45.2 | 36 | 9.1 | 6.6 | 5.2 |
| 50 KVA | 40 | 139 | 132 | 120 | 77 | 66.5 | 60 | 48 | 12.1 | 8.8 | 7 |
| 62.5 KVA | 50 | 173 | 165 | 152 | 96 | 83 | 76 | 61 | 15.1 | 10.9 | 8.7 |
| 75 KVA | 60 | 208 | 198 | 181 | 115 | 99.5 | 91 | 72 | 18.1 | 13.1 | 10.5 |
| 93.8 KVA | 75 | 261 | 247 | 226 | 143 | 123 | 113 | 90 | 22.6 | 16.4 | 13 |
| 100 KVA | 80 | 278 | 264 | 240 | 154 | 133 | 120 | 96 | 24.1 | 17.6 | 13.9 |
| 125 KVA | 100 | 347 | 330 | 301 | 192 | 166 | 150 | 120 | 30 | 21.8 | 17.5 |
| 156 KVA | 125 | 433 | 413 | 375 | 240 | 208 | 188 | 150 | 38 | 27.3 | 22 |
| 187 KVA | 150 | 520 | 495 | 450 | 288 | 249 | 225 | 180 | 45 | 33 | 26 |
| 219 KVA | 175 | 608 | 577 | 527 | 335 | 289 | 264 | 211 | 53 | 38 | 31 |
| 250 KVA | 200 | 694 | 660 | 601 | 384 | 332 | 301 | 241 | 60 | 44 | 35 |
| 312 KVA | 250 | 866 | 825 | 751 | 480 | 415 | 376 | 300 | 75 | 55 | 43 |
| 375 KVA | 300 | 1040 | 990 | 903 | 576 | 498 | 451 | 361 | 90 | 66 | 52 |
| 438 KVA | 350 | 1220 | 1155 | 1053 | 672 | 581 | 527 | 422 | 105 | 77 | 61 |
| 500 KVA | 400 | 1390 | 1320 | 1203 | 770 | 665 | 602 | 481 | 120 | 88 | 69 |
| 625 KVA | 500 | 1735 | 1650 | 1504 | 960 | 830 | 752 | 602 | 150 | 109 | 87 |
| 750 KVA | 600 | 2080 | 1980 | 1803 | 1150 | 996 | 902 | 721 | 180 | 131 | 104 |
| 875 KVA | 700 | 2430 | 2310 | 2104 | 1344 | 1274 | 1052 | 842 | 210 | 153 | 121 |
| 1000 KVA | 800 | 2780 | 2640 | 2405 | 1540 | 1330 | 1203 | 962 | 241 | 176 | 139 |
| 1125 KVA | 900 | 3120 | 2970 | 2709 | 1730 | 1495 | 1354 | 1082 | 271 | 197 | 156 |
| 1250 KVA | 1000 | 3470 | 3300 | 3009 | 1920 | 1660 | 1504 | 1202 | 301 | 218 | 174 |
| 1563 KVA | 1250 | 4350 | 4130 | 3740 | 2400 | 2080 | 1885 | 1503 | 376 | 273 | 218 |
| 1875 KVA | 1500 | 5205 | 4950 | 4520 | 2880 | 2490 | 2260 | 1805 | 452 | 327 | 261 |
| 2188 KVA | 1750 | 5280 | 3350 | 2890 | 2640 | 2106 | 528 | 380 | 304 | ||
| 2500 KVA | 2000 | 6020 | 3840 | 3320 | 3015 | 2405 | 602 | 436 | 348 | ||
| 2812 KVA | 2250 | 6780 | 4320 | 3735 | 3400 | 2710 | 678 | 491 | 392 | ||
| 3125 KVA | 2500 | 7520 | 4800 | 4160 | 3740 | 3005 | 752 | 546 | 435 | ||
| 3750 KVA | 3000 | 9040 | 5760 | 4980 | 4525 | 3610 | 904 | 654 | 522 | ||
| 4375 KVA | 3500 | 10550 | 6700 | 5780 | 5285 | 4220 | 1055 | 760 | 610 | ||
| 5000 KVA | 4000 | 12040 | 7680 | 6640 | 6035 | 4810 | 1204 | 872 | 695 | ||
kVA stands for Kilovolt-Ampere and is the rating regularly utilized to rate a transformer. The size of a transformer is decided by the kVA of the load. In numerous circumstances the power required by the load is proportionate to the rating of the transformer communicated in either VA or kVA. For case a 1KW (1000 Watts) load would require a 1kVA transformer @ unity power factor.
KVA calculation
For three phase KVA= (V*I*1.732)/1000
For single phase KVA= (V*I)/1000
MVA calculation-
For three phase MVA= (V*I*1.732)/100,000
For single phase MVA= (V*I)/1000,000
| Main Technical Parameters for 11/10.5/10/6.3/6KV level ,S11 series distribution transformer | ||||||
| Rated Power (kva) |
High Voltage (kv) |
H.V.Tap range |
Low Voltage (kv) |
Connection symbol |
No-load loss(W) | On-load loss(W) |
| 30 |
6
6.3
10
10.5
11
|
±5
±2*2.5 |
0.4
|
Yyn0 | 0.10 | 0.60/0.63 |
| 50 |
Yyn0
Dyn11
Yzn1 |
0.13 | 0.87/0.91 | |||
| 63 | 0.15 | 1.04/1.00 | ||||
| 80 | 0.18 | 1.25/1.31 | ||||
| 100 | 0.20 | 1.50/1.58 | ||||
| 125 | 0.24 | 1.80/1.89 | ||||
| 160 | 0.27 | 2.20/2.31 | ||||
| 200 | 0.33 | 2.60/2.73 | ||||
| 250 | 0.40 | 3.05/3.2 | ||||
| 315 | 0.48 | 3.65/3.83 | ||||
| 400 | 0.57 | 4.30/4.52 | ||||
| 500 | 0.68 | 4.15/5.41 | ||||
| 630 |
Yyn0
Dyn11 |
0.81 | 6.20 | |||
| 800 | 0.98 | 7.50 | ||||
| 1000 | 1.16 | 10.30 | ||||
| 1250 | 1.37 | 12.00 | ||||
| 1600 | 1.65 | 14.50 | ||||
| 2000 | 1.96 | 19.8 | ||||
| Rated voltage ratio(V) | Accuracy class and rated secondary output(VA) | Max.output | Rated insulation level(KV) | ||||
| 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.2/0.5 | 0.5/0.5 | 6P | |||
|
3000 100 100 √3 √3 |
60 | 120 | / | / | 100 | 1000 | 3.6/25/40 |
|
6000 100 100 √3 √3 |
7.2/32/60 | ||||||
|
10000 100 100 √3 √3 |
75 | 150 | 1500 | 12/42/75 | |||
|
6000 100 100 100 √3 √3 √3 |
/ | / | 50/80 | 90/90 | 1000 | 7.2/32/60 | |
|
10000 100 100 100 √3 √3 √3 |
75/120 | 120/120 | 1500 | 12/42/75 | |||
| Power | Max Voltage | Weight of Oil | Active Section Weight | Total Weight | Leng. A | Wid. B | Heig. C | D | F | ØG | L | M | N | S | T |
| kVA | kV | kg | kg | kg | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm |
| 315 KVA | 6,3-11 | 245 | 820 | 1295 | 1525 | 750 | 1740 | 1035 | 670 | 150 | 50 | 310 | 330 | 178 | 150 |
| 15 | 270 | 840 | 1315 | 1540 | 760 | 1750 | 1040 | 385 | 330 | ||||||
| 33 | 295 | 850 | 1330 | 1600 | 775 | 1805 | 1105 | 485 | 350 | ||||||
| 400 KVA | 6,3-11 | 255 | 910 | 1360 | 1370 | 775 | 1595 | 1070 | 670 | 150 | 50 | 310 | 265 | 138 | 150 |
| 15 | 290 | 960 | 1460 | 1495 | 775 | 1710 | 1115 | 385 | 265 | ||||||
| 33 | 335 | 965 | 1525 | 1600 | 775 | 8155 | 1155 | 485 | 330 | ||||||
| 500 KVA | 6,3-11 | 300 | 1100 | 160 | 1600 | 760 | 1700 | 1150 | 670 | 150 | 50 | 310 | 330 | 263 | 150 |
| 15 | 315 | 1145 | 1690 | 1625 | 775 | 1765 | 1165 | 385 | 330 | ||||||
| 33 | 380 | 1175 | 1800 | 1675 | 805 | 1920 | 1220 | 485 | 350 | ||||||
| 630 KVA | 6,3-11 | 350 | 1280 | 1900 | 1680 | 790 | 1785 | 1185 | 670 | 150 | 50 | 310 | 330 | 263 | 150 |
| 15 | 340 | 1285 | 1895 | 1640 | 785 | 1780 | 1185 | 385 | 330 | ||||||
| 33 | 440 | 1405 | 2135 | 1700 | 810 | 1945 | 1255 | 485 | 350 | ||||||
| 800 KVA | 6,3-11 | 480 | 1530 | 2335 | 1860 | 945 | 1835 | 1190 | 820 | 150 | 50 | 310 | 400 | 263 | 150 |
| 15 | 475 | 1585 | 2385 | 1845 | 925 | 1870 | 1225 | 385 | |||||||
| 33 | 560 | 1625 | 2515 | 1950 | 925 | 2000 | 1255 | 485 | |||||||
| 1000 KVA | 6,3-11 | 540 | 1760 | 2690 | 1910 | 990 | 1900 | 1330 | 820 | 200 | 70 | 310 | 400 | 340 | 150 |
| 15 | 565 | 1840 | 2780 | 1915 | 965 | 1975 | 1330 | 385 | |||||||
| 33 | 650 | 1855 | 2900 | 1950 | 1015 | 2090 | 1360 | 485 | |||||||
| 1250 KVA | 6,3-11 | 685 | 2070 | 3345 | 2050 | 1010 | 2025 | 1380 | 820 | 200 | 70 | 310 | 400 | 340 | 150 |
| 15 | 670 | 2080 | 3345 | 2015 | 995 | 2090 | 1400 | 385 | |||||||
| 33 | 760 | 2130 | 3495 | 2005 | 1005 | 2245 | 1455 | 485 | |||||||
| 1600 KVA | 6,3-11 | 825 | 2415 | 4010 | 2100 | 1130 | 2110 | 1420 | 820 | 200 | 70 | 310 | 400 | 372 | 200 |
| 15 | 855 | 2545 | 4155 | 2020 | 1125 | 2110 | 1420 | 385 | |||||||
| 33 | 1000 | 2858 | 4405 | 2090 | 1185 | 2245 | 1455 | 485 | |||||||
| 2000 KVA | 6,3-11 | 1025 | 2730 | 4785 | 2265 | 1250 | 2255 | 1525 | 1000 | 200 | 70 | 310 | 400 | 372 | 200 |
| 15 | 1080 | 2765 | 4895 | 2270 | 1260 | 2160 | 1430 | 385 | |||||||
| 33 | 1185 | 2745 | 4985 | 2270 | 1275 | 2465 | 1635 | 485 | |||||||
| 2500 KVA | 6,3-11 | 1420 | 3645 | 6300 | 2395 | 1710 | 2365 | 1625 | 1000 | 200 | 70 | 310 | 400 | 450 | 330 |
| 15 | 1445 | 3630 | 6300 | 2395 | 1710 | 2380 | 1640 | 385 | |||||||
| 33 | 1485 | 3625 | 6345 | 2395 | 1410 | 2525 | 1690 | 485 |
Cable size is fundamentally chosen by the current it is assumed to carry, and the voltage for which it is utilized. In expansion, frequently the voltage drop passable from one conclusion to the other moreover has to be inside limits. So on HV/ LV sides cables have to be chosen with these considerations. Only specify of 500 KVA transformer isn’t sufficient, though in most likelihood, you must be referring to 11 KV/ 440 V transformer.
Cable current carrying capacity:
Transformer full load current is calculated by:
Ifull-load = 12.5 × 106 / 1.73 × 20 × 103 = 361 A
How to use the full load chart to find kVA
A) Determine the secondary voltage of your transformer.
B) Sum up the total amperes required by the load.
C) From the full load current table below, select a transformer under the corresponding secondary voltage, with a standard kVA capacity and amperage equal to or higher than the sum required by the load.
| kVA | Current in Amperes | ||||||
| 120V | 240V | 416V | 480V | 600V | 2400V | 4160V | |
| 0.25 | 2.08 | 1.04 | 0.6 | 0.52 | 0.41 | – | – |
| 0.5 | 4.16 | 2.08 | 1.2 | 1.04 | 0.83 | – | – |
| 0.75 | 6.25 | 3.13 | 1.8 | 1.56 | 1.25 | – | – |
| 1 | 8.33 | 4.17 | 2.4 | 2.08 | 1.67 | – | – |
| 1.5 | 12.5 | 6.25 | 3.6 | 3.13 | 2.5 | – | – |
| 2 | 16.7 | 8.33 | 4.81 | 4.17 | 3.33 | – | – |
| 3 | 25 | 12.5 | 7.21 | 6.25 | 5 | 1.25 | 0.72 |
| 5 | 41.6 | 20.8 | 12 | 10.4 | 8.33 | 2.08 | 1.2 |
| 7.5 | 62.5 | 31.2 | 18 | 15.6 | 12.5 | 3.12 | 1.8 |
| 10 | 83.3 | 41.6 | 24 | 20.8 | 16.6 | 4.16 | 2.4 |
| 15 | 125 | 62.5 | 36 | 31.2 | 25 | 6.25 | 3.6 |
| 25 | 208 | 104 | 60 | 52 | 41.6 | 10.4 | 6 |
| 37.5 | 312 | 156 | 90.1 | 78.1 | 62.5 | 15.6 | 9.01 |
| 50 | 416 | 208 | 120 | 104 | 83.3 | 20.8 | 12 |
| 75 | 625 | 312 | 180 | 156 | 125 | 31.2 | 18 |
| 100 | 833 | 416 | 240 | 208 | 166 | 41.6 | 24 |
| 150 | 1250 | 625 | 360 | 312 | 250 | 62.5 | 36 |
| 167 | 1391 | 695 | 401 | 347 | 278 | 69.5 | 40.1 |
| 250 | 2083 | 1041 | 600 | 520 | 416 | 104 | 60 |
| 333 | 2775 | 1387 | 800 | 693 | 555 | 138 | 80 |
Single Phase AC Motor Full Load Running Currents in Amperes and Recommended Transformer Ratings
| Horsepower | Full Load Current (Amps) | Minimum Transformer KVA | ||
| 110-120V | 208V | 220-240V* | ||
| 0.5 | 9.8 | 5.4 | 4.9 | 1.5 |
| 0.75 | 13.8 | 7.6 | 6.9 | 2 |
| 1 | 16 | 8.8 | 8 | 3 |
| 1.5 | 20 | 11 | 10 | 3 |
| 2 | 24 | 13.2 | 12 | 5 |
| 3 | 34 | 18.7 | 17 | 5 |
| 5 | 56 | 30.8 | 28 | 7.5 |
| 7.5 | 80 | 44 | 40 | 15 |
| 10 | 100 | 55 | 50 | 15 |
| 15 | 135 | 74.8 | 68 | 25 |
| 20 | – | – | 88 | 25 |
| 25 | – | – | 110 | 37.5 |
| 30 | – | – | 136 | 37.5 |
| 40 | – | – | 176 | 50 |
| 50 | – | – | 216 | 75 |
kVA ratings include 10% overcapacity for frequent motor starts.
*For 200 volt motors, increase 220-240V ratings by 15%.
| kVA | Current in Amperes | |||||||
| 208V | 240V | 380V | 416V | 480V | 600V | 2400V | 4160V | |
| 2 KVA | 5.55 | 4.81 | 3.03 | 2.77 | 2.4 | 1.92 | 0.48 | 0.27 |
| 3 KVA | 8.32 | 7.21 | 4.55 | 4.16 | 3.6 | 2.88 | 0.72 | 0.41 |
| 6 KVA | 16.6 | 14.4 | 9.11 | 8.32 | 7.21 | 5.77 | 1.44 | 0.83 |
| 9 KVA | 24.9 | 21.6 | 13.6 | 12.4 | 10.8 | 8.66 | 2.16 | 1.24 |
| 15 KVA | 41.6 | 36 | 22.7 | 20.8 | 18 | 14.4 | 3.6 | 2.08 |
| 30 KVA | 83.2 | 72.1 | 45.5 | 41.6 | 36 | 28.8 | 7.21 | 4.16 |
| 45 KVA | 124 | 108 | 68.3 | 62.4 | 54.1 | 43.3 | 10.8 | 6.24 |
| 75 KVA | 208 | 180 | 113 | 104 | 90.2 | 72.1 | 18 | 10.4 |
| 112.5 KVA | 312 | 270 | 170 | 156 | 135 | 108 | 27 | 15.6 |
| 150 KVA | 416 | 360 | 227 | 208 | 180 | 144 | 36 | 20.8 |
| 225 KVA | 624 | 541 | 341 | 312 | 270 | 216 | 54.1 | 31.2 |
| 300 KVA | 832 | 721 | 455 | 416 | 360 | 288 | 72.1 | 41.6 |
| 450 KVA | 1249 | 1082 | 683 | 624 | 541 | 433 | 108 | 62.4 |
| 500 KVA | 1387 | 1202 | 759 | 693 | 601 | 481 | 120 | 69.3 |
| 600 KVA | 1665 | 1443 | 911 | 832 | 721 | 577 | 144 | 83.2 |
| 750 KVA | 2081 | 1804 | 1139 | 1040 | 902 | 721 | 180 | 104 |
Three Phase AC Motor Full Load Running Currents in Amperes and Recommended Transformer Ratings
| Horsepower | Full Load Current (Amps) Minimum | Transformer kVA | ||||
| 110-120V | 208V | 220-240V* | 440-480V | 550-600V | ||
| 0.5 | 4 | 2.2 | 2 | 1 | 0.8 | 3 |
| 0.75 | 5.6 | 3.1 | 2.8 | 1.4 | 1.1 | 3 |
| 1 | 7.2 | 4 | 3.6 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 3 |
| 1.5 | 10.4 | 5.7 | 5.2 | 2.6 | 2.1 | 3 |
| 2 | 13.6 | 7.5 | 6.8 | 3.4 | 2.7 | 6 |
| 3 | 19.2 | 10.7 | 9.6 | 4.8 | 3.9 | 6 |
| 5 | 30.4 | 16.7 | 15.2 | 7.6 | 6.1 | 9 |
| 7.5 | 44 | 24 | 22 | 11 | 9 | 15 |
| 10 | 56 | 31 | 28 | 14 | 11 | 15 |
| 15 | 84 | 46 | 42 | 21 | 17 | 30 |
| 20 | 108 | 59 | 54 | 27 | 22 | 30 |
| 25 | 136 | 75 | 68 | 34 | 27 | 45 |
| 30 | 160 | 88 | 80 | 40 | 32 | 45 |
| 40 | 208 | 114 | 104 | 52 | 41 | 75 |
| 50 | 260 | 143 | 130 | 65 | 52 | 75 |
| 60 | – | 170 | 154 | 77 | 62 | 75 |
| 75 | – | 211 | 192 | 96 | 77 | 112.5 |
| 100 | – | 273 | 248 | 124 | 99 | 150 |
kVA ratings include 10% overcapacity for frequent motor starts.
* For 200 volt motors, increase 220-240V ratings by 15%.
|
|






